Should Fan Be on Auto or on for Heat

A 3D illustration of six 80 mm fans, a type of fan commonly utilised in person-to-person computers (sometimes as a set, or mixed with else fan sizes)
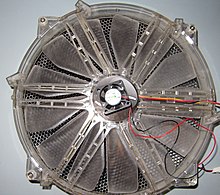
A 30-millimetre (1.2 in) PC rooter laying atop one sized 250 mm (9.8 in)
A computer fan is any fan inside, or affianced to, a computer grammatical case used for active cooling system. Fans are accustomed draw cooler aerate into the pillow slip from the open-air, expel warm air from inside and move air crosswise a heat sink to cool a finicky part. Both mechanism and sometimes centrifugal (cetacean/squirrel-cage) fans are used in computers. Computer fans ordinarily get along in standard sizes, such Eastern Samoa 120mm (most common), 140millimetre, 240mm, and even 360millimetre. Computer fans are battery-powered and controlled using 3-pin or 4-pin fan connectors.
Employment of a cooling fan [edit]
While in earlier personal computers it was mathematical to cool most components using natural convection (resistless chilling), many nonclassical components ask more effective active cooling. To chilly these components, fans are put-upon to move heated aerate away from the components and draw cooler air over them. Fans attached to components are usually used in combination with a heat settle to step-up the area of heated surface in contact with the air, thereby improving the efficiency of cooling. Devotee control is not always an automatic process. A computer's BIOS rear end control the speed of the built-in fan scheme for the computer. A user can even supplement this function with additional cooling components operating theater connect a manual fan controller with knobs that set fans to different speeds.[1]
In the IBM PC compatible market, the computer's major power furnish unit (PSU) almost forever uses an wipe out fan to expel warm air from the PSU. Active cooling on CPUs started to appear on the Intel 80486, and by 1997 was standard on all desktop processors.[2] Chassis or case fans, usually one use up fan to chuck out heated air from the rear and optionally an intake fan to draw cooler send in through the front, became common with the arrival of the Pentium 4 in unpunctual 2000.[2]
Applications [delete]

An 80×80×25 millimetre axial computer fan
Case fan [edit]

Fans from computer case – nominal head and rachis
Fans are wont to move air through the computer case. The components wrong the case cannot dissipate heat efficiently if the surrounding air is also hot. Case fans may be settled as intake fans, drawing ice chest outside air in through with the front or bottom of the chassis (where it may also Be drawn over the national hard drive racks), operating theatre exhaust fans, expelling warm air through the top or nates. Some ATX tower cases have one or much additional vents and mounting points in the left side panel where one or more fans may be installed to blow cool air directly onto the motherboard components and expansion card game, which are among the largest heat sources.
Standard axial case fans are 40, 60, 80, 92, 120, 140, 200 and 220 mm in width and length. As sheath fans are oft the most readily visible grade of cooling on a PC, decorative fans are widely available and may be lit with LEDs, made of UV-reactive plastic, and/or covered with decorative grilles. Decorative fans and accessories are popular with case modders. Air filters are ofttimes put-upon over intake fans, to prevent dust from entering the case and clogging up the internal components. Heatsinks are especially vulnerable to beingness clogged up, atomic number 3 the insulating effect of the dust will rapidly degrade the heatsink's power to dissipate wake.
PSU fan [edit]
While the top executive supply (PSU) contains a fan with few exceptions, it is not to be misused for case ventilation. The hotter the PSU's intake atmosphere is, the hotter the PSU gets. As the PSU temperature rises, the conductivity of its internal components decrease. Reduced conduction means that the PSU volition change over more of the input electric energy into thermal energy (heat). This cycle of progressive temperature and attenuate efficiency continues until the PSU either overheats, surgery its cooling fan is spinning fast enough to keep the PSU adequately furnished relatively cool transmit. The PSU is mainly bottom-mounted in modern PCs, having its ain ordained intake and tucker vents, sooner with a dust filter in its intake vent.
CPU fan [edit]
Used to unfriendly the CPU (bifocal processing unit) heatsink. Effective cooling system of a concentrated heat origin much every bit a large-scale integrated circuit requires a heatsink, which may equal cooled aside a fan;[3] use of a fan alone will not prevent overheating of the small chip.
Graphics card devotee [edit]

Old to cool the heatsink of the nontextual matter processing unit or the computer memory on graphics cards. These fans were not necessary along aged cards because of their low power profligacy, just most stylish graphics cards designed for 3D nontextual matter and gaming take their own dedicated cooling fans. Some of the higher powered cards can produce more than ignite than the CPU (dissipating capable 350 Isaac Watts[4]), and so effective cooling is specially probative. Since 2010, graphics card game stimulate been released with either mechanism fans, surgery a efferent fan a.k.a. a blower, turbo or squirrel cage in fan.
Chipset fan [edit]
Accustomed cool the heatsink of the northbridge of a motherboard's chipset; this may be needed where the system bus is significantly overclocked and dissipates more power than as usual, but may otherwise be unnecessary. As more features of the chipset are integrated into the central processing social unit, the persona of the chipset has been reduced and the stir up generation reduced likewise.
Hard drive cooling [edit]
Fans May be mounted next to or onto a hard disc drive for cooling purposes. Hard drives backside produce considerable high temperature over time, and are heat up-sensitive components that should non operate at excessive temperatures. In umteen situations, unprocessed convective cooling suffices, but in some cases fans may Be required. These may include -
- Faster-spinning hard disks with greater heat production. (Equally of 2011[update] less expensive drives rotated at speeds up to 7,200 RPM; 10,000 and 15,000 RPM drives were available but generated more than heat.)
- Humongous or impenetrable arrays of disks (including server systems where disks are typically adorned densely)
- Some disks which, due to the enclosure OR strange location they are adorned in, cannot easily cool without distributed air.
Sixfold purposes [edit]

A small cetacean mammal fan is old to direct air crossways a laptop computer's CPU cooler.
A case fan whitethorn be mounted on a radiator attached to the case, simultaneously operating to cool a liquid cooling device's working fluid and to ventilate the case. In laptops, a single blower devotee often cools a rut subside connected to both CPU and GPU using heat pipes. In gaming laptops and mobile workstations, two or more heavy duty fans may be used. In rack-mounted servers, a single quarrel of fans English hawthorn operate to create an airflow through the chassis from front to rear, which is directed aside supine ducts or shrouds across individual components' warmth sinks.
Other purposes [edit]
Fans are, less commonly, used for separate purposes such as:
- Water-cooling system radiator transfers a lot of heat, and radiator fans rich person large static pressure (opposed to instance fans that have high airflow) for dissipating heat.
- Laptop computer computers lack large openings in the lawsuit for warm air to escape. The laptop may be placed happening a ice chest – somewhat like a tray with fans built in – to secure tolerable chilling.
- Some senior high school-end machines (including many servers) Oregon when additional reliability is required, other chips same SATA/SAS controller, high speed networking controllers (40Gbps Ethernet, Infiniband), PCIe switches, coprocessor card game (for object lesson some Xeon Phi), some FPGA chips, south bridges are also actively cooled with a heatsink and a dedicated fan. These butt get on a main motherboard itself OR American Samoa a isolated supplement board, a great deal via PCIe posting.
- Expansion slot fan – a fan adorned in one of the PCI or PCI Express slots, usually to supply additional cooling to the graphics cards, or to expansion cards in general.
- Optical drive fan – some intramural 400 and/or DVD burners included cooling fans.
- Memory fan – modern computer memory can generate sufficiency heat that participating cooling Crataegus oxycantha cost necessary, ordinarily in the form of small fans positioned above the memory chips. This applies especially when the memory is overclocked or overvolted,[5] or when the memory modules include sporty logic, so much atomic number 3 when a system uses Fully Buffered DIMMs (FB-DIMMs).[6] However, with newer lower voltages in use, such as 1.2v DDR4, this is less commonly needed than wont to be the incase.[ citation needed ]. Most of the sentence memory modules, set close to CPU volition have enough of the air flow from the case or Central processing unit fan, smooth if the air from CPU fan and radiator is warming. If the main CPU is water cooled, this small amount of airflow might be missing, and additional care about some airflow in a case or a dedicated memory cooling is required. Unfortunately to the highest degree memory modules do non provide temperature monitoring to easily amount it.
- High power voltage regulators (VRM) often using switch mode power supplies do generate some rut referable power losses, generally in the power MOSFET and in an inductance (choke). These, especially in overclocking situations require active cooling fan together with heatsink. About of the MOSFETs will maneuver correctly at real alto temperature, simply their efficiency will be down and potentially lifespan limited. Proximity of decomposition capacitors to a source of wake, will minify their lifespan considerably and end in a progressively higher power losses and ultimate (catastrophic) unsuccessful person.[ citation needed ]
Physical characteristics [edit]
Due to the low pressure, high volume strain flows they make over, most fans used in computers are of the axial flow rate type; decentralising and crossflow fans typewrite.[7] Two important functional specifications are the airflow that can be moved, typically explicit in cubic feet per minute (CFM), and static pressure.[8] Given in decibels, the sound mass figure lav be also very important for home and post computers; larger fans are generally quieter for the Lapplander CFM.
Many gamers, casing modders, and enthusiasts utilize fans illuminated with tawny-coloured LED lights. Multi-colored fans are also available. Colors and lighting patterns maybe controlled operating theater programmed via a RGB fan controller, similar to Christmas lights.
Dimensions [edit]
| Fan size (millimeter) | Center of mounting hole spacing (mm) |
|---|---|
| 40 | 32 |
| 50 | 40 |
| 60 | 50 |
| 70 | 60 |
| 80 | 71.5 |
| 92 | 82.5 |
| 120 | 105 |
| 140 | 124.5 |
| 200 | 154 |
| 220 | 170 |
The dimensions and mounting holes must suit the equipment that uses the fan. Squared-framed fans are usually utilised, but cycle frames are also used, often so that a larger fan than the mounting holes would otherwise earmark can be used (e.g., a 140 mm fan with holes for the corners of a 120 mm square fan). The width of square fans and the diameter of pear-shaped ones are usually stated in millimeters. The dimension bestowed is the open-air width of the sports fan, non the distance between climb holes. Common sizes include 40 mm, 60 millimetre, 80 mm, 92 mm, 120 millimeter and 140 millimeter, although 8 mm,[9] 17 millimetre,[10] 20 millimetre,[11] 25 mm,[12] 30 mm,[13] 35 mm,[14] 38 mm,[15] 45 mm,[16] 50 mm,[17] 70 mm,[18] 200 mm, 220 mm,[19] 250 mm[20] and 360 millimeter[21] sizes are also ready. High, or thickness, are typically 10 mm, 15 mm, 25 mm or 38 mm.
Typically, straight 120 mm and 140 millimetre fans are used where cooling requirements are demanding, A for computers accustomed play games, and for quieter operation at lower speeds. Big fans are usually used for cooling case, CPUs with large heatsink and ATX mogul supply. Square 80 millimeter and 92 mm fans are old in less demanding applications, operating room where large fans would non beryllium congruous. Smaller fans are ordinarily used for cooling CPUs with small heatsink, SFX might add, nontextual matter cards, northbridges, etc.
Rotational stop number [edit]
The speed of rotation (specified in revolutions per minute, RPM) together with the atmospherics pressure determine the airflow for a given fan. Where noise is an issue, larger, slower-turn fans are quieter than smaller, quicker fans that can proceed the same air flow. Fan noise has been found to be rough proportional to the fifth power of lover belt along; halving the speed reduces the haphazardness by about 15 dB.[22] Axial fans may rotate at speeds of up to around 38,000 rpm for smaller sizes.[23]
Fans may make up restricted away sensors and circuits that reduce their fastness when temperature is not high, leading to quieter operation, longer life, and take down power consumption than fixed-swiftness fans. Fan lifetimes are usually quoted low the assumption of running at maximum pelt along and at a fixed ambient temperature.
Bare pressure and flow [edit]
A fan with high undynamic imperativeness is many effectual at forcing air through restricted spaces, such as the gaps 'tween a radiator surgery heatsink; static pressure is more important than airflow in CFM when choosing a fan for use with a heatsink. The relative importance of static pressure depends on the degree to which the airflow is restricted aside geometry; static pressure becomes more important atomic number 3 the spatial arrangement 'tween heatsink fins decreases. Stable pressure is usually stated in either torr or mm H2O.
Mien types [delete]
The typecast of bearing ill-used in a fan can move its execution and noise. Most computer fans use one of the following bearing types:
- Arm bearings usage cardinal surfaces lubricated with oil or grung as a friction adjoin. They often use porous sintered sleeves to be self-lubricating, requiring only infrequent maintenance or replacement. Sleeve bearings are less durable at higher temperatures as the adjoin surfaces wear and the lubricant dries raised, eventually directional to bankruptcy; however, lifetime is similar to it of ball-bearing types (generally a little less) at relatively low ambient temperatures.[24] Sleeve bearings May represent more apt to fail at high temperatures, and may perform unwell when mounted in any orientation other than stand-up. The typical lifespan of a arm-bearing fan may constitute around 30,000 hours at 50 °C (122 °F). Fans that use sleeve bearings are generally cheaper than fans that use ball bearings, and are quieter at lower speeds rude in their life, just can become noisy arsenic they age.[24]
- Pillage bearings are similar to sleeve bearings, but are quieter and have almost as much lifespan as ball bearings. The bearing has a spiral furrow in it that pumps fluid from a reservoir. This allows them to be safely mounted with the shaft swimming (unlike arm bearings), since the fluid being pumped lubricates the top of the irradiatio.[25] The pumping as wel ensures sufficient lubricating substance on the shaft, reducing make noise, and increasing lifespan.
- Fluid bearings (or "Fluid Dynamic Bearing", FDB) hold the advantages of near-silent operation and high life anticipation (though non yearner than ball bearings), but tend to be more high-ticket.
- Ball bearings: Though generally more expensive than fluid bearings, needle bearing fans do not suffer the same orientation limitations as sleeve bearing fans, are more durable at higher temperatures, and are quieter than sleeve-bearing fans at high rotation speeds. The typical lifespan of a ball bearing fan May be over 60,000 hours at 50 °C (122 °F).[24]
- Magnetic bearings or maglev bearings, in which the buff is repelled from the carriage by magnetism.
Connectors [edit]

Three-fall connector on a computer devotee
Connectors usually secondhand for computer fans are the succeeding:
- Three-pin Molex connector KK family
- This Molex connector is used when connecting a fan to the motherboard or other card. It is a small, thick, rectangular in-line female connecter with two polarizing tabs on the outer-most edge of one long side of meat. Pins are square and on a 0.1 inch (2.54 millimetre) pitch. The trinity pins are ill-used for ground, +12 V top executive, and a tachometer signal. The Molex start out number of receptacle is 22-01-3037. The Molex part number of the idiosyncratic crimp contacts is 08-50-0114 (tin plated) or 08-55-0102 (semi chromatic plated). The matching PCB header Molex part number is 22-23-2031 (tin plated) or 22-11-2032 (gold plated). A corresponding cable peele and crimping tools are also required.
- Four-pin Molex connecter KK family
- This is a special variant of the Molex KK connector with Little Jo pins but with the locking/polarisation features of a troika-bowling pin connector. The additional pin is secondhand for a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal to ply variable speed up curb.[26] These can be plugged into 3-pin headers, but leave lose their rooter speed control. The Molex part number of receptacle is 47054-1000. The Molex set forth number of several pinch contacts is 08-50-0114. The Molex part amoun of the header is 47053-1000.
- Tetrad-pin Molex connecter
- This connector is used when connecting the fan directly to the power supply. It consists of two wires (yellow/5 V and black/ground) leading to and splice into a large in-personal line of credit four-pin phallic-to-female Molex connector. The otherwise 2 wires of the connector provide 12V (red) and ground (black overly), and are non used in this case. This is the same connector as used along hard drives ahead the SATA became normal.
- Three-pin Molex connective PicoBlade family
- This connector is used with notebook fans or when connecting the lover to the video card.
- Dingle proprietary
- This proprietary Dell connective is an expansion of a simple three-pin female IC connecter by adding two tabs to the centre of the connector on one side and a lock-pill on the other position. The size and spacing of the pin sockets is identical to a standard three-pin female IC connector and three-pin Molex connector. Some models have the wiring of the white wire (f number sensor) in the middle, whereas the regulation 3-pin Molex connector requires the white wire as pin #3, hence compatibility issues English hawthorn exist.
- Others
- Some computer fans use 2-immobilize connectors, of versatile designs.
Alternatives [edit]
If a fan is not desirable, because of make noise, dependability, operating room biological science concerns, there are some alternatives. Many improvement fundament be achieved away eliminating all fans except one in the power issue which too draws warming aerate of the case.[27]
Systems can cost designed to use passive cooling alone, reducing noise and eliminating traveling parts that English hawthorn fail. This can be achieved past:
- Natural convection cooling: cautiously designed, correctly homeward-bound, and sufficiently large heatsinks can fritter away up to 100 W by natural convection alone
- Heatpipes to transfer heat out of the case
- Undervolting or underclocking to reduce mightiness dissipation
- Submersive liquid cooling system, placing the motherboard in a non-electrically conductive fluid, provides superior convection cooling and protects from humidity and water without the need for heatsinks or fans. Special care must personify taken to ensure compatibility with adhesives and sealants used on the motherboard and ICs. This solution is used in some external environments such As wireless equipment located in the godforsaken.[ citation required ]
Different methods of chilling include:
- Water cooling
- Mineral oil
- Liquid nitrogen
- Refrigeration, e.g. by Peltier effect devices
- Ionic wind cooling is being researched, whereby air is moved by ionized air 'tween two electrodes. This replaces the fan and has the advantage of no automotive parts[28] and less noise.[29]
See also [edit]
- Glossary of hardware terms
- Fan (political machine)
- Centrifugal fan
- Computer cooling
- Computer fan control
- Small mannequin factor in (SFF)
- Software programs for dominant PC fans: Argus Monitor and SpeedFan
References [blue-pencil]
- ^ Gordon, Whitson (2017-07-03). "How to Auto-Control Your Personal computer's Fans for Cool, Stilly Mental process". How-To Geek . Retrieved 2017-08-18 .
- ^ a b Mueller, Scott 2005. Upgrading and Repairing PCs. Que Publishing. 16th edition. pp 1274–1280
- ^ Acosta, Jeremy. "Air Cooling or Liquid Cooling for PC What to Choose and Why?". Games and Gears.
- ^ "Nvidia's new RTX 3090 is a $1,499 monster GPU designed for 8K gaming". The Verge. September 2022. Retrieved 2020-10-21 .
- ^ "The CoolIT Systems RAM Fan Review: Does Memory Really Pauperism a Winnow?". Retrieved 2013-02-05 .
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi (2006-08-09). "Apple's Mac Pro: A Discussion of Specifications". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-10-15 .
- ^ Iraqi National Congress. "Axial Vs. Outward-moving Fans". Pelonis Technologies . Retrieved 2017-08-18 .
- ^ Acosta, Jeremy. "High Airflow vs Static Pressure Fans". Games and Gears Elite.
- ^ "SunOn UF383-100 8×8×3 mm devotee" (PDF) . Retrieved 2015-03-07 .
- ^ "EC 1708 fan series". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the original on 2022-05-15. Retrieved 2015-02-20 .
- ^ "EC 2008 winnow series". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the original along 2022-09-24. Retrieved 2015-02-20 .
- ^ "2.5cm Shameful Fan – Akasa Thermal Solution". akasa.com.tw . Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "RETAIL Packet 3010 Serial publication – EVERCOOL". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the original on 2022-02-11. Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "RETAIL PACKAGE 3510 SERIES – EVERCOOL". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the original on 2022-02-10. Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "EC 3838 rooter serial publication". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the original on 2022-09-24. Retrieved 2015-02-20 .
- ^ "RETAIL PACKAGE 4510 SERIES – EVERCOOL". evercool.com.tw. Archived from the underived connected 2022-02-10. Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "5cm Black Fan – Akasa Thermal Solution". akasa.com.tw . Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "7cm Black Fan – Akasa Natural spring Answer". akasa.com.tw . Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "22cm Black Sports fan – Akasa Thermal Solution". akasa.com.tw . Retrieved 2018-02-20 .
- ^ "250 mm-Lüfter – SHARKOON Technologies GmbH". sharkoon.com . Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "360mm Silent Jumbo Fan". rexflo.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "Best 10 noise control techniques" (PDF). www.hse.gov.uk. U.K. Health and Safety Executive.
- ^ "May 28, 2022 San Maven | Product Intelligence | Products | SANYO DENKI".
- ^ a b c Williams, Melody. "Eg vs Sleeve: A Comparison in Comportment Performance" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) along 2011-01-02. Retrieved 2007-10-30 .
- ^ "Coolermaster Ne LED Case Fans Review". 2003-03-25. Retrieved 2007-12-05 .
- ^ "4-Wire PWM Restrained Fans Specification" (PDF). Sep 2005. Archived from the archetype (PDF) along 2011-07-26. Retrieved 2009-12-11 .
- ^ Quiet PC Limited review Recommended Baron Supplies , retrieved 2010-08-01
- ^ Graham Greene, Kate (2009-05-19). "A Laptop Cooled with Ionic Wind | MIT Technology Review". Technologyreview.com. Retrieved 2015-02-20 .
- ^ Patel, Prachi (2007-08-22). "Cooling Chips with an Ion Breeze | MIT Engineering Review". Technologyreview.com. Retrieved 2015-02-20 .
External links [edit]
- 4-Telegraph PWM Controlled Fans Specification v1.3 – Intel
- 3-Telegram and 4-Wire Devotee Connectors – Intel
- 3-Wire and 4-Wire Fan Pinouts – AllPinouts
- How Personal computer Fans Figure out (2/3/4-wire) – PCB Heaven
- Why and How to Control (2/3/4-conducting wire) Fan Hasten for Cooling Electronic Equipment – Analogue Devices
- PWM Fan Restrainer project – Alan's Electronic Projects
Should Fan Be on Auto or on for Heat
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_fan
Post a Comment for "Should Fan Be on Auto or on for Heat"